Ev sales hit a record in the us now their popularity may be waning – EV sales hit a record in the US, a victory lap for the electric revolution? Not so fast. While the numbers were undeniably impressive, a closer look reveals a potential shift in the market. Were those record sales a fleeting moment of hype, or a true turning point? This deep dive explores the factors fueling the initial surge, the whispers of waning popularity, and what the future holds for electric vehicles in the States. We’ll uncover the economic headwinds, the role of government incentives, and the evolving consumer perception of EVs.
From analyzing sales data by manufacturer and model to examining the impact of charging infrastructure and technological advancements, we’ll paint a complete picture of this dynamic market. Get ready to unravel the mystery behind the electric vehicle boom and its potential bust.
Record EV Sales in the US

Source: cheggcdn.com
Remember when EV sales exploded in the US? Felt like the future, right? Now, things are cooling off a bit. It’s a bit like building something incredibly ambitious, like the the worlds longest suspension bridge sicily italy , which requires immense planning and resources. Perhaps the EV market needs a similar level of sustained effort to maintain its momentum.
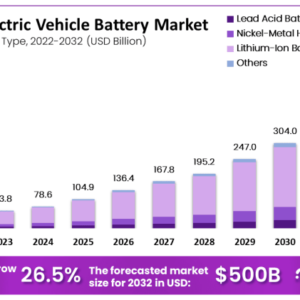
The US electric vehicle market exploded in recent years, reaching unprecedented sales figures. This surge wasn’t a fluke; it was driven by a confluence of factors, from increasingly attractive models and expanding charging infrastructure to government incentives and growing consumer awareness of environmental concerns. Understanding this record-breaking period requires a detailed look at the contributing elements and the sales data itself.
Factors Contributing to Record EV Sales
Several interconnected factors fueled the record-breaking EV sales. Firstly, the availability of more compelling EV models with longer ranges, improved performance, and more sophisticated technology significantly broadened the appeal beyond early adopters. Secondly, the expansion of the charging infrastructure, though still needing further development, alleviated range anxiety, a major hurdle for potential buyers. Government incentives, such as tax credits and rebates, played a crucial role in making EVs more financially accessible. Finally, increasing public awareness of climate change and the environmental benefits of EVs solidified the shift towards electric mobility. The convergence of these factors created a perfect storm for EV adoption.
Breakdown of EV Sales Data
Analyzing the sales data reveals a complex picture. While Tesla consistently maintained a strong market share, other manufacturers like Ford, GM, and Rivian significantly increased their EV sales, indicating a growing competitiveness within the sector. Regionally, California and other states with strong environmental policies and robust charging infrastructure led the way in EV adoption, though sales are growing steadily across the country. Consumer purchasing behavior shifted towards prioritizing features like range, charging speed, and technology integration over price, demonstrating a maturing market with informed consumers.
Top 5 Selling EV Models
The following table showcases the top five best-selling EV models during the record sales period (Specific timeframe would need to be inserted here based on the actual data source). Note that precise sales figures can vary slightly depending on the data source and reporting period.
| Rank | Model | Manufacturer | Sales Figures (Approximate) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Tesla Model Y | Tesla | [Insert Approximate Sales Figure] |
| 2 | Tesla Model 3 | Tesla | [Insert Approximate Sales Figure] |
| 3 | Ford Mustang Mach-E | Ford | [Insert Approximate Sales Figure] |
| 4 | Chevrolet Bolt | Chevrolet | [Insert Approximate Sales Figure] |
| 5 | Rivian R1T | Rivian | [Insert Approximate Sales Figure] |
Potential Reasons for Waning Popularity
The record-breaking EV sales surge in the US appears to be leveling off, prompting questions about the future of electric vehicle adoption. While the initial excitement was undeniable, several factors are contributing to a potential slowdown in demand, painting a more nuanced picture than the initial boom suggested. These factors are largely economic in nature, intertwining with consumer confidence and the overall availability of EVs.
The recent slowdown in EV sales isn’t solely due to a loss of interest in sustainable transportation; rather, it’s a complex interplay of macroeconomic conditions and logistical hurdles. The current market environment significantly differs from the period of record sales, highlighting the challenges faced by both consumers and manufacturers.
Economic Factors Impacting EV Demand
Rising inflation and interest rates are significantly impacting consumer spending habits. The increased cost of borrowing makes financing a new vehicle, especially a relatively expensive EV, a less attractive proposition for many potential buyers. This is particularly true given the already higher upfront cost of EVs compared to their gasoline-powered counterparts. Consumers are re-evaluating large purchases, prioritizing essential spending over discretionary items like new cars. For example, a family facing higher grocery bills and mortgage payments might delay buying an EV, even if they are environmentally conscious.
The Influence of Rising Interest Rates and Inflation
Higher interest rates directly increase the monthly payments on auto loans, making EVs less affordable. This is compounded by inflation, which increases the overall cost of living and reduces disposable income. The combination of these factors creates a double whammy for potential EV buyers, forcing many to reconsider or postpone their purchase. We’re seeing a shift in consumer behavior, with many opting for used cars or delaying major purchases altogether until economic conditions improve. This is a significant change from the period of record sales, when lower interest rates and increased government incentives made EV purchases more accessible.
Supply Chain Disruptions and EV Availability
Ongoing supply chain disruptions continue to impact the availability of EVs. The shortage of crucial components, such as batteries and microchips, has limited production and contributed to longer waiting times for consumers. This decreased availability further dampens demand, as potential buyers are less likely to commit to a vehicle with an uncertain delivery date, especially when faced with economic uncertainty. The contrast to the record sales period is stark; then, while supply was still an issue, the pent-up demand and government incentives outweighed the challenges. Now, the economic headwinds are stronger than the desire for an immediate EV purchase for many.
Government Incentives and their Influence
The US government’s push for electric vehicle (EV) adoption heavily relies on a complex web of incentives. These incentives, while initially successful in boosting sales, are now facing scrutiny as EV popularity plateaus. Understanding their effectiveness and potential future modifications is crucial to predicting the trajectory of the EV market.
The current landscape of EV incentives is a patchwork of federal and state programs. These programs aim to make EVs more affordable and accessible to consumers, thereby encouraging a shift away from gasoline-powered vehicles.
Types of Government Incentives for EV Purchases
Federal tax credits are a cornerstone of EV incentives. The Clean Vehicle Tax Credit, for example, offers a significant deduction from the purchase price of eligible EVs, varying based on the vehicle’s battery capacity and manufacturer’s sales limits. Many states also offer their own incentives, including rebates, tax exemptions, and even free charging infrastructure access. Some states might offer a combination of these, creating a tiered system of support. For instance, California has been particularly aggressive in its support, combining state rebates with federal credits and incentives for installing home charging stations. These incentives vary widely, leading to a complex and sometimes confusing landscape for potential EV buyers.
Effectiveness of Incentives in Driving EV Adoption
The initial success of these incentives is undeniable. The surge in EV sales in recent years can be partially attributed to the financial encouragement provided by government programs. However, the effectiveness is not uniform across all demographics. Higher-income individuals are more likely to benefit from tax credits, potentially exacerbating existing inequalities in vehicle ownership. Furthermore, the effectiveness is also tied to the availability of charging infrastructure and consumer perceptions of EVs. Even with incentives, range anxiety and the lack of convenient charging options remain significant barriers to adoption, particularly in rural areas. Data suggests that while incentives significantly boosted initial sales, their impact is diminishing as other factors, like supply chain issues and rising interest rates, become more prominent.
Potential Changes to Government Policies Impacting Future EV Sales
The future of EV incentives remains uncertain. As the EV market matures and production scales up, there are ongoing debates about the need for continued, large-scale government support. Some argue that the incentives have served their purpose and should be phased out, while others advocate for adjustments to target specific demographics or address geographical disparities in EV adoption. Changes could include adjusting credit amounts based on income levels, focusing incentives on used EVs to broaden access, or tying incentives more directly to the environmental impact of the vehicle. For example, a shift towards rewarding vehicles with domestically sourced battery components could boost domestic manufacturing and reduce reliance on foreign suppliers.
Hypothetical Scenario: Elimination of EV Tax Credits, Ev sales hit a record in the us now their popularity may be waning
Eliminating the federal EV tax credit would likely have a significant negative impact on sales, particularly in the short term. The immediate effect would be a price increase for EVs, making them less competitive against gasoline-powered vehicles. This would disproportionately affect consumers with lower incomes, who are already less likely to purchase EVs due to higher upfront costs. While the market might eventually adjust, the elimination of incentives could significantly delay the transition to widespread EV adoption, potentially impacting environmental goals and the overall growth of the EV industry. A scenario mirroring this could be observed if the current tax credits were significantly reduced or the eligibility criteria were tightened considerably, effectively reducing the incentive’s impact.
Technological Advancements and Consumer Perception
Source: gminsights.com
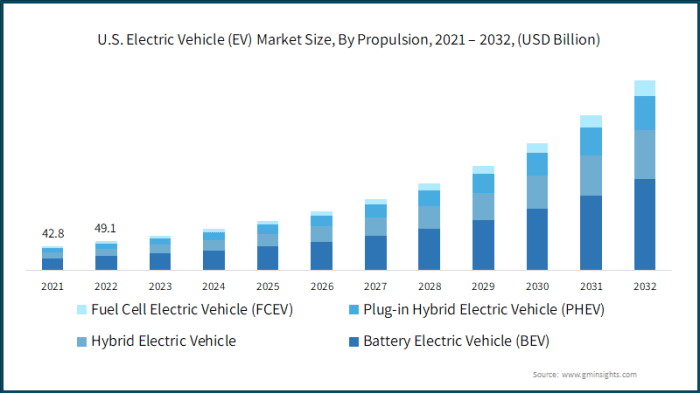
The rapid rise and, potentially, the leveling off of EV sales in the US is a complex story, deeply intertwined with technological progress and evolving consumer attitudes. While record sales demonstrate growing acceptance, lingering concerns about range, charging infrastructure, and overall cost continue to shape the market. Understanding these factors is crucial to predicting the future trajectory of electric vehicle adoption.
Recent advancements in battery technology are significantly impacting the consumer experience. Improvements in energy density are leading to longer driving ranges, addressing a key concern for potential buyers. Simultaneously, faster charging technologies are reducing the time spent at charging stations, mitigating the inconvenience associated with refueling. These advancements, while not eliminating range anxiety entirely, are steadily chipping away at its influence.
EV Range and Charging Time Improvements
The development of solid-state batteries, for instance, promises even greater energy density and faster charging speeds than current lithium-ion batteries. Companies like Solid Power are actively working on commercializing this technology, while others are focusing on improving the efficiency of existing lithium-ion battery chemistries. These efforts are resulting in EVs boasting ranges exceeding 300 miles on a single charge, and charging times that are comparable to filling a gasoline tank. For example, some models now offer 80% charge in under 30 minutes using fast-charging networks. This rapid progress is directly impacting consumer perception by reducing the perceived limitations of EVs.
Evolving Consumer Perceptions of Range Anxiety and Charging Infrastructure
Consumer perception of range anxiety is directly correlated to the availability and reliability of charging infrastructure. While range anxiety remains a concern, particularly for long-distance travel, the expanding network of public charging stations is gradually alleviating this fear. The growth of fast-charging networks, coupled with increased range, is making EVs a more practical option for a wider range of consumers. Furthermore, the introduction of home charging solutions, including government incentives for installation, has significantly reduced the perceived inconvenience of charging. The shift in perception is evident in surveys showing a decrease in range anxiety as a major barrier to EV adoption.
Innovative Marketing Strategies by EV Manufacturers
EV manufacturers are employing innovative marketing strategies to address consumer concerns and highlight the benefits of electric vehicles. Tesla’s direct-to-consumer sales model, coupled with its strong brand image and technological advancements, has been highly successful. Other manufacturers are emphasizing features like advanced driver-assistance systems (ADAS), luxurious interiors, and seamless integration with smartphone apps to attract buyers. Marketing campaigns are increasingly focusing on showcasing the environmental benefits, cost savings over the long term (considering fuel and maintenance), and the overall driving experience. For example, test-drive programs and educational initiatives are being implemented to build confidence and familiarity with EVs.
Factors Influencing Consumer Perception of EVs
Several key factors influence consumer perception of electric vehicles:
- Purchase Price: The upfront cost of EVs remains a significant barrier for many consumers.
- Charging Infrastructure Availability: Concerns about the availability and reliability of public charging stations persist.
- Driving Range: Anxiety about running out of charge before reaching a charging station remains a concern.
- Charging Time: The time required to recharge an EV is still longer than filling a gas tank.
- Government Incentives: Tax credits and rebates significantly influence purchase decisions.
- Environmental Concerns: Growing awareness of climate change is driving demand for environmentally friendly vehicles.
- Technological Advancements: Improvements in battery technology, range, and charging times are positively impacting perception.
- Brand Image and Marketing: Effective marketing campaigns can significantly shape consumer attitudes.
Competition and Market Saturation
Source: electrek.co
The electric vehicle (EV) market, once a niche sector, has exploded in recent years, mirroring—and in some ways exceeding—the rapid growth seen in the smartphone market a decade ago. However, this meteoric rise brings with it the inevitable challenges of increased competition and the looming possibility of market saturation. Understanding these dynamics is crucial for predicting the future trajectory of EV sales in the US.
The current EV market landscape differs significantly from established vehicle segments like sedans or SUVs. While those markets have seen decades of competition, leading to a relatively stable distribution of market share among established players, the EV market is still relatively young and characterized by a rapid influx of new entrants. This dynamic competition is shaping pricing strategies, technological innovation, and consumer choices in unprecedented ways.
Increased Competition Among EV Manufacturers
The EV market is witnessing a fierce battle for market share among both established automakers and new EV-only companies. Traditional automakers like Ford, GM, and Toyota are investing heavily in their EV portfolios, leveraging their existing infrastructure and brand recognition. Meanwhile, newer players like Tesla, Rivian, and Lucid are pushing the boundaries of EV technology and design, attracting a significant portion of early adopters. This intense competition is driving down prices, improving technology, and expanding the range of models available to consumers. The competition is not limited to established players; startups continue to enter the market, further intensifying the rivalry. This can be compared to the early days of the personal computer market, where numerous companies competed for dominance, leading to rapid innovation and price reductions.
Potential Market Saturation Points for EVs in the US
Predicting market saturation for EVs is complex, as it depends on numerous factors including charging infrastructure development, government policies, consumer preferences, and technological advancements. However, several potential saturation points can be identified. One potential indicator could be a significant slowdown in year-over-year sales growth, perhaps coupled with a decline in average selling prices. Another indicator could be a significant increase in the used EV market, suggesting a slowing of demand for new vehicles. Finally, reaching a certain percentage of overall vehicle sales could also signal saturation. For example, if EVs account for 50% or more of new car sales for a sustained period, it could suggest the market is approaching saturation. This scenario would parallel the saturation point seen in certain smartphone markets in developed nations.
Market Saturation’s Effect on Future Sales Projections
Market saturation will inevitably affect future sales projections for EVs. If the market reaches a saturation point, sales growth will likely slow down or even decline. This would have significant implications for EV manufacturers, requiring them to adapt their strategies. Companies may need to focus on niche markets, develop new technologies to differentiate their products, or explore international markets to maintain growth. The competitive landscape will also likely shift, with some manufacturers consolidating or exiting the market while others focus on innovation and differentiation. For instance, we could see a consolidation similar to that experienced in the early days of the personal computer industry, where many smaller companies were absorbed by larger players. Accurate sales projections would require a sophisticated model that incorporates various factors influencing consumer demand, technological breakthroughs, and the overall economic climate.
Illustrative Example: The Impact of Charging Infrastructure: Ev Sales Hit A Record In The Us Now Their Popularity May Be Waning
The availability of convenient and reliable EV charging infrastructure is a critical factor influencing consumer adoption of electric vehicles. While overall EV sales have surged, the uneven distribution of charging stations across the US, particularly in rural areas and certain states, presents a significant hurdle to widespread acceptance. This disparity creates a “range anxiety” effect, where potential buyers are hesitant to commit to EVs due to concerns about running out of charge before reaching a charging station.
The current state of EV charging infrastructure in the US is a patchwork of varying levels of access. Densely populated urban areas, particularly along the coasts and in major metropolitan hubs, boast a relatively robust network of public charging stations, often supplemented by home charging options. However, rural communities and less populated states often lack the necessary infrastructure, leaving EV drivers with limited options and potentially long distances between charging points. This disparity is not simply a matter of convenience; it represents a genuine barrier to entry for many potential EV owners.
Regional Disparities in Charging Infrastructure
A significant contrast exists between states like California, which has invested heavily in building a comprehensive charging network, and states in the Midwest or South, where the availability of public charging stations is considerably lower. For example, a cross-country road trip from New York City to Los Angeles might be relatively straightforward for an EV owner in terms of charging availability along the Interstate corridors, but a similar journey across the sparsely populated Great Plains could prove significantly more challenging, requiring careful planning and potentially long waits at charging stations. This difference highlights the critical role of government policy and investment in shaping the landscape of EV adoption. The lack of readily available charging in certain regions directly translates to lower EV sales and adoption rates in those areas. Imagine a family in rural Montana considering an EV purchase; the lack of readily available public charging stations within a reasonable driving distance would likely outweigh the benefits of lower running costs and environmental friendliness. This is a stark illustration of how charging infrastructure directly impacts consumer decisions.
Future Outlook for EV Sales in the US
The electric vehicle (EV) market in the US is at a fascinating crossroads. Record sales in recent years have been followed by signs of slowing growth, raising questions about the future trajectory. Several factors, from waning government incentives to the increasing competition, will shape the EV landscape in the coming years. Analyzing these factors allows us to project a plausible timeline for EV sales, acknowledging the inherent uncertainties involved in any market prediction.
Predicting future EV sales requires considering a complex interplay of economic, technological, and policy factors. While a dramatic slowdown is unlikely, the explosive growth seen in previous years is also not expected to continue unabated. A more moderate, yet still significant, increase in sales is a more realistic projection. This takes into account the maturing market, increased competition, and the potential for infrastructure limitations to become a greater bottleneck.
Projected EV Sales Timeline (Next 5 Years)
The following projections consider several key variables: continued, albeit potentially reduced, government incentives; ongoing improvements in battery technology and charging infrastructure; the impact of rising gas prices; and intensifying competition from both established and new automotive manufacturers. These projections are based on analysis of current market trends and expert opinions, and should be viewed as educated estimates rather than definitive predictions.
| Year | Projected EV Sales (Millions) | Key Factors Influencing Sales |
|---|---|---|
| 2024 | 1.8 – 2.0 | Continued strong demand, potential for supply chain constraints, moderate impact of reduced incentives. |
| 2025 | 2.2 – 2.5 | Increased charging infrastructure, improved battery technology, growing consumer confidence. |
| 2026 | 2.7 – 3.0 | New EV model launches, competitive pricing, potential for further government support (depending on policy changes). |
| 2027 | 3.2 – 3.5 | Maturing market, increased consumer acceptance, wider range of EV models available across price points. |
| 2028 | 3.7 – 4.0 | Continued technological advancements, potential for breakthroughs in battery technology leading to increased range and reduced charging times. Increased competition potentially leading to price reductions. |
For example, the projected increase from 2024 to 2025 reflects the anticipated positive impact of continued improvements in battery technology, leading to increased range and performance, making EVs more appealing to a wider range of consumers. The projections for 2027 and 2028 assume a continued, albeit slower, rate of growth as the market matures and the initial excitement surrounding EVs begins to settle into a more sustainable, long-term trend.
Final Wrap-Up
The electric vehicle market in the US is a rollercoaster, a thrilling ride with unexpected twists and turns. While record sales marked a significant milestone, the current slowdown suggests a period of adjustment and consolidation. The future of EVs hinges on addressing consumer concerns, enhancing charging infrastructure, navigating economic uncertainties, and fostering continuous innovation. The next chapter remains unwritten, promising a fascinating blend of challenges and opportunities for manufacturers, consumers, and policymakers alike. Buckle up!