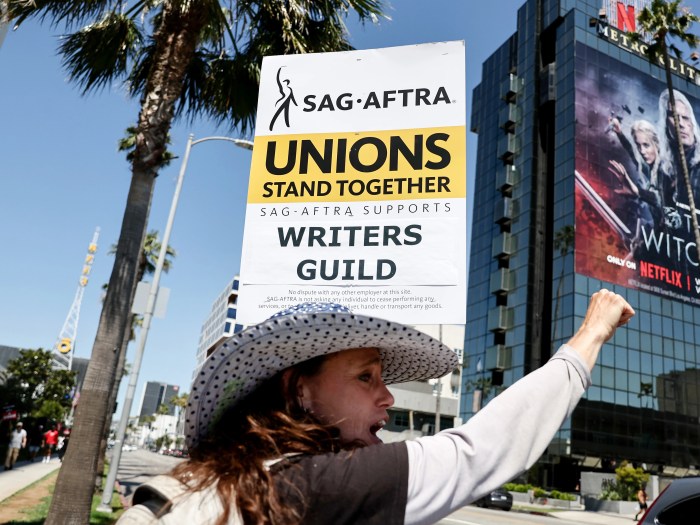
Hollywood screenwriters artificial intelligence guardrails: The rise of AI in Hollywood is rewriting the script, literally. From brainstorming to final drafts, AI tools offer unprecedented potential, boosting productivity and unlocking creative avenues. But this technological leap isn’t without its bumps. Ethical dilemmas, copyright concerns, and the very definition of authorship are all being challenged. This exploration delves into the necessary guardrails to ensure AI enhances, not erodes, the art of screenwriting.
We’ll examine the potential benefits – think faster drafting, innovative story structures, and even democratized access to screenwriting tools. But we’ll also confront the downsides – the risk of homogenized narratives, job displacement anxieties, and the complex legal landscape surrounding AI-generated content. The goal? To navigate the exciting, yet treacherous, path towards a future where humans and AI collaborate creatively, ethically, and legally.
The Impact of AI on Screenwriting

Source: co.uk
The rise of artificial intelligence is shaking up Hollywood, and screenwriting is no exception. AI tools, once a futuristic fantasy, are now readily available, promising to revolutionize the creative process – but also raising significant concerns about the future of human writers. This exploration delves into the potential benefits and drawbacks of AI in screenwriting, examining how it might alter the very nature of storytelling.
Potential Benefits of AI Tools for Screenwriters
AI offers screenwriters a range of powerful tools to enhance their craft. These tools can assist with tasks like generating story ideas, developing character arcs, outlining plots, and even writing initial drafts. Imagine an AI that can analyze thousands of scripts to identify successful plot structures, or one that can suggest dialogue options based on character personalities and relationships. This frees up the screenwriter’s time and energy, allowing them to focus on the more nuanced aspects of storytelling – the emotional core, thematic depth, and unique voice that truly distinguish a great script. AI can act as a powerful brainstorming partner, pushing creative boundaries and offering fresh perspectives that might otherwise be missed. For example, an AI could analyze a screenwriter’s existing work and suggest unexplored narrative avenues or thematic connections, potentially leading to a richer and more complex story.
Potential Drawbacks of AI Tools for Screenwriters
While AI offers exciting possibilities, it also presents potential pitfalls. The most significant concern is the risk of homogenization. If screenwriters rely too heavily on AI tools, there’s a danger that scripts will begin to feel formulaic and lack originality. The unique voices and perspectives of individual writers could be lost in a sea of AI-generated content. Furthermore, issues of copyright and ownership are still largely unresolved. Who owns the intellectual property when a script is co-written by a human and an AI? And what happens when an AI generates a script that is strikingly similar to an existing work, raising concerns about plagiarism? The potential for job displacement is another significant worry. As AI becomes more sophisticated, there’s a risk that studios might opt for cheaper, AI-generated scripts, leaving human screenwriters out of work.
Comparison of Creative Processes: Screenwriters Using AI vs. Those Who Don’t
A screenwriter using AI might approach their work with a more iterative and collaborative mindset. They might start by using AI to generate initial ideas or Artikels, then refine and personalize those ideas with their own creative input. This process could lead to faster script development, but might also involve a greater reliance on technology and less reliance on pure intuition. In contrast, a screenwriter who doesn’t use AI may rely more heavily on traditional methods, such as freewriting, mind-mapping, and extensive research. Their process may be slower, but it might also foster a deeper connection with the story and characters, resulting in a more emotionally resonant script. The difference boils down to a collaborative versus a solitary approach to the creative process.
Hypothetical Scenario Illustrating Both Positive and Negative Impacts
Imagine Sarah, a struggling screenwriter. She uses AI to help her Artikel a sci-fi thriller. The AI suggests a compelling plot twist she hadn’t considered, significantly strengthening the story. This helps her land a meeting with a studio executive, leading to a lucrative contract. However, during production, the studio decides to use the AI to generate additional scenes, resulting in a less nuanced and ultimately less successful film. Sarah’s name is on the script, but the creative control she initially had is significantly diminished, leading to frustration and a sense of compromised artistic integrity. This exemplifies how AI can both boost a screenwriter’s career and simultaneously undermine their creative control and artistic vision.
Necessary Guardrails for AI in Screenwriting
The rise of AI in screenwriting presents exciting possibilities, but also significant ethical and legal challenges. Unfettered use could lead to unintended consequences, impacting creativity, copyright, and the very fabric of the filmmaking industry. Establishing clear guardrails is crucial to ensure responsible innovation and prevent potential harms.
Ethical Concerns in AI-Generated Screenplays
Three key ethical concerns emerge from the use of AI in screenwriting: bias in generated content, the potential displacement of human screenwriters, and questions surrounding originality and ownership. AI models are trained on existing data, which may reflect societal biases. This can lead to the perpetuation of stereotypes and harmful representations in AI-generated scripts. Furthermore, the increasing capabilities of AI raise concerns about job displacement for human screenwriters. Finally, determining the ownership of AI-generated screenplays presents a complex legal and ethical challenge.
Guidelines for Responsible AI Usage in Screenwriting
The following table Artikels guidelines for responsible AI usage in the screenwriting process, addressing potential drawbacks and mitigation strategies.
| Concern | Proposed Solution | Potential Drawback of Solution | Mitigation Strategy |
|---|---|---|---|
| Bias in AI-generated content | Train AI models on diverse and representative datasets; implement bias detection and mitigation techniques during the development and deployment phases. | Complete elimination of bias is difficult; residual biases may remain undetected. | Regular audits of AI outputs for bias; human review and editing to identify and correct biases. Transparency about the limitations of the AI and the steps taken to mitigate bias. |
| Job displacement of human screenwriters | Frame AI as a tool to augment, not replace, human creativity; focus on training and upskilling screenwriters to work effectively with AI. | Resistance from screenwriters to adopting AI tools; difficulty in predicting the long-term impact on employment. | Invest in education and training programs for screenwriters; promote collaboration between humans and AI. Focus on AI’s ability to handle repetitive tasks, freeing up human writers for more creative work. |
| Originality and ownership of AI-generated content | Establish clear guidelines on copyright and ownership; consider models where human screenwriters retain primary authorship even when using AI assistance. | Legal ambiguity surrounding AI-generated works; difficulty in defining the extent of human contribution. | Develop clear legal frameworks for AI-generated content; establish transparent attribution practices; prioritize collaboration and human oversight to ensure clear lines of authorship. |
Maintaining Human Oversight in AI-Assisted Screenwriting
Human oversight is paramount in the AI-assisted screenwriting process. While AI can assist with tasks like generating plot Artikels, dialogue, or even entire scenes, it lacks the nuanced understanding of human emotion, storytelling conventions, and cultural context necessary for creating truly compelling narratives. Human writers must retain control over the creative direction, ensuring the final product reflects their vision and artistic intent. AI should be a tool to enhance, not replace, human creativity. Think of it as a sophisticated word processor, not a replacement for the writer. A skilled screenwriter using AI tools can produce more polished and efficient work.
Legal Ramifications of Unattributed AI-Generated Content
Using AI-generated content without proper attribution raises significant legal risks. Copyright law is still evolving in the context of AI, but using AI-generated material without acknowledging its source could lead to copyright infringement claims, especially if the AI model was trained on copyrighted works. Furthermore, misrepresenting AI-generated content as wholly original human work could lead to legal and reputational damage. Transparency and proper attribution are crucial to navigate the evolving legal landscape of AI-generated content. Consider the case of a screenwriter using an AI tool to generate dialogue. If that dialogue is substantially similar to existing copyrighted dialogue, the screenwriter could face legal action.
AI’s Role in Different Stages of Screenwriting
Source: presencesecure.com
Hollywood screenwriters are grappling with AI guardrails, worried about creative control in the face of rapidly advancing technology. This creative control debate echoes discussions in game development, as highlighted in this insightful legend of zelda tears of the kingdom fujibayashi aonuma interview about balancing innovation with artistic vision. Ultimately, the challenge for both industries is to harness AI’s potential without sacrificing the human element that makes storytelling truly compelling.
The rise of artificial intelligence is shaking up Hollywood, and screenwriting is no exception. While AI won’t replace the human touch – the emotional core, the unique voice – it’s rapidly becoming a powerful tool capable of streamlining the often grueling process of bringing stories to life. From initial brainstorming to final revisions, AI offers a range of functionalities that can significantly boost a screenwriter’s efficiency and creativity.
AI’s assistance in screenwriting spans the entire creative journey, acting as a versatile collaborator rather than a replacement for the human element. It can help manage the overwhelming logistical aspects of writing, allowing screenwriters to focus on the more nuanced aspects of storytelling – character development, plot twists, and emotional resonance. This collaborative approach allows for a more efficient and potentially more innovative writing process.
AI Assistance in Brainstorming and Outlining
AI can be invaluable during the initial stages of screenplay development. Tools can generate plot ideas based on specified genres, character archetypes, or even s related to the desired theme. For example, inputting “sci-fi thriller with a female protagonist and a time-travel element” could yield multiple plot Artikels, each offering a different narrative structure and potential conflict points. These Artikels can then be further refined and developed by the screenwriter, acting as a springboard for creative exploration. AI can also help structure the screenplay, suggesting logical sequences of events and ensuring a compelling narrative arc. Think of it as a highly organized and efficient brainstorming partner, generating multiple possibilities that a human might overlook.
AI Applications for Dialogue Generation and Character Development
AI’s ability to analyze vast datasets of existing scripts allows it to generate realistic and nuanced dialogue. By feeding the AI information about character personalities, relationships, and the overall tone of the screenplay, a screenwriter can receive suggestions for dialogue that fit the context and maintain consistency. Similarly, AI can assist in character development by suggesting traits, motivations, and backstories based on the desired character arc. For example, an AI could suggest a compelling backstory for a seemingly ordinary character, adding depth and complexity to their role within the narrative. This can be especially useful when a screenwriter is struggling to fully flesh out a character or needs to ensure consistency in their actions and dialogue throughout the screenplay.
AI Tools for Different Screenwriting Stages
The effective use of AI in screenwriting depends on choosing the right tool for each stage of the process.
- Concept Stage: Tools focusing on idea generation and world-building are most helpful here. Examples include AI that can generate plot Artikels, character profiles, and even initial scene descriptions based on user prompts.
- First Draft Stage: AI can assist with dialogue generation, scene structuring, and ensuring narrative consistency. Tools might offer suggestions for improving pacing, identifying potential plot holes, or suggesting alternative dialogue options.
- Revisions Stage: AI can analyze the completed draft for pacing issues, inconsistencies in character development, or clichés. It can also provide suggestions for improving the overall readability and impact of the script.
AI-Driven Script Analysis and Trend Identification
AI can analyze a large corpus of existing scripts to identify prevalent themes, character archetypes, plot structures, and dialogue patterns. This can help screenwriters understand current trends in the industry, identify potential clichés to avoid, and gain insights into what resonates with audiences. For example, by analyzing successful action films, an AI could identify common plot points, character types, and dialogue styles that contribute to their success. This data can then be used to inform the creation of new scripts, ensuring they align with audience expectations while still maintaining originality. This analytical capability can be a valuable tool for market research and understanding audience preferences.
The Future of AI and Screenwriting Collaboration
The synergy between human creativity and artificial intelligence in screenwriting is poised to redefine the industry. We’re not talking about robots replacing writers, but rather a powerful partnership where AI becomes a sophisticated tool, augmenting human abilities and accelerating the creative process. This evolution will not only impact the way stories are crafted but also democratize access to storytelling for a wider range of voices.
The role of the screenwriter will undoubtedly evolve in this AI-assisted landscape. Instead of solely focusing on crafting every line of dialogue and scene description, screenwriters will likely become more akin to architects of narrative, overseeing the overall structure, thematic elements, and emotional arc of a project. They’ll curate and refine the output of AI tools, focusing on the nuanced aspects of character development, emotional resonance, and overall storytelling that currently elude even the most advanced algorithms. Think of it as a shift from meticulous craftsmanship to strategic orchestration.
AI’s Democratization of Screenwriting Tools
AI has the potential to significantly lower the barrier to entry for aspiring screenwriters. Expensive software, extensive industry knowledge, and access to established networks are currently significant hurdles. AI-powered tools can offer affordable, accessible resources, such as script generation assistance, grammar and style checks, and even initial plot outlining, enabling individuals from diverse backgrounds and economic circumstances to participate in the screenwriting world. Imagine a world where a talented writer in a remote village has the same access to sophisticated scriptwriting tools as a seasoned professional in Hollywood. This accessibility could lead to a more diverse and inclusive range of stories being told. Examples of this already exist with platforms offering AI-powered grammar and style assistance, though more sophisticated tools are needed for a true democratization.
A Glimpse into the Future Hollywood Writers’ Room, Hollywood screenwriters artificial intelligence guardrails
Imagine a brightly lit, modern writers’ room. Large, interactive screens dominate one wall, displaying dynamic storyboards, character profiles generated by AI, and potential plot trajectories visualized as branching narratives. Writers are seated around a central table, each equipped with a personalized tablet displaying their own AI-powered scriptwriting interface. This interface allows for real-time collaboration, suggesting dialogue options, flagging potential plot holes, and offering stylistic alternatives. A central AI hub processes data from various sources, including audience analytics, trending topics, and even competitor scripts, providing insights to inform the creative process. The room is less about individual writing and more about a collective, fluid process of co-creation between humans and AI, constantly refining and improving the script. The atmosphere is collaborative and energetic, leveraging the strengths of both human creativity and the analytical power of AI. The writers are not competing with the AI, but using it as a powerful partner in the creative process.
Addressing Copyright and Ownership Concerns: Hollywood Screenwriters Artificial Intelligence Guardrails
The rise of AI in screenwriting introduces a fascinating legal grey area: who owns the copyright to a screenplay partially or wholly generated by an AI? This question throws existing copyright law into sharp relief, forcing a re-evaluation of authorship, originality, and the very definition of creative work. The potential for disputes is immense, impacting both the creators using the AI and the studios potentially profiting from the output.
The core problem stems from the nature of copyright itself, which traditionally protects “original works of authorship” fixed in a tangible medium. AI, however, doesn’t possess authorship in the human sense. It learns from existing data, creating outputs that are statistically probable but not necessarily uniquely original. This raises the question: can something lacking human intent and creativity be truly copyrighted? Furthermore, the training data used by AI often comprises copyrighted material itself, creating a potential for derivative works and infringement claims.
Copyright Issues Arising from AI Use in Screenwriting
AI-generated screenplays can infringe on existing copyrights in several ways. First, if the AI is trained on a massive dataset including copyrighted screenplays, novels, or other creative works, the resulting output might inadvertently incorporate elements that constitute copyright infringement. This could manifest as similar plot points, character archetypes, or even verbatim dialogue. Second, even if the AI generates a seemingly original screenplay, the question of whether it meets the threshold of originality required for copyright protection remains. The current legal framework is ill-equipped to handle this level of nuance. Finally, the use of AI tools in the editing and revision process can also blur the lines of authorship and raise questions about the extent of human contribution required for copyright protection. For instance, if a human writer uses AI to significantly rewrite or refine a script, determining the balance of contribution between human and machine becomes crucial for ownership.
Solutions for Determining Ownership of AI-Assisted Screenplays
Determining ownership of AI-assisted screenplays requires a multifaceted approach. One possibility is to adopt a “work made for hire” doctrine, assigning ownership to the individual or entity commissioning the AI-generated screenplay. This approach, however, needs careful consideration to prevent exploitation of AI developers and creators. Alternatively, a system of co-ownership could be established, granting rights to both the human user and the AI developer, possibly based on a pre-agreed percentage. This requires clear contracts and a robust framework for resolving potential disputes. A third approach might involve creating a new legal category specifically for AI-generated works, establishing distinct ownership rules and guidelines. This new category would require careful consideration to ensure it is both practical and prevents loopholes that could be exploited.
Comparison of Existing Copyright Laws and Challenges Posed by AI-Generated Content
Existing copyright laws, primarily designed for human-created works, struggle to accommodate AI-generated content. The concept of “authorship” is central to copyright, and AI lacks the capacity for independent creative thought. This raises fundamental questions about the applicability of existing copyright laws. Furthermore, the difficulty in tracing the sources used by AI in its training data complicates the identification of potential copyright infringements. Existing laws offer little guidance on the appropriate level of originality required for an AI-generated work to qualify for copyright protection. A significant challenge is the potential for mass-produced, AI-generated content to overwhelm the copyright system, leading to increased litigation and reduced incentives for human creativity.
Hypothetical Legal Case: AI-Generated Screenplay
Imagine a case where a screenwriter uses an AI tool to generate a screenplay. The screenplay becomes a blockbuster, generating millions in revenue. The AI developer claims a share of the profits, arguing that their algorithm played a significant role in creating the screenplay’s success. The screenwriter, meanwhile, argues that they provided the initial prompts and made significant edits, thus holding primary ownership. The studio might also claim rights based on their production and distribution efforts. The court would need to determine the level of originality contributed by the AI, the extent of human intervention, and the nature of the contractual agreements between the parties involved. The outcome could vary widely, setting important precedents for future cases. The court might rule in favor of the screenwriter, emphasizing the importance of human creativity, or it might establish a precedent for shared ownership or a new legal framework for AI-generated works, potentially leading to significant changes in copyright law.
Last Word

Source: geeknack.com
The integration of AI into Hollywood screenwriting is inevitable, but its success hinges on responsible development and implementation. Establishing clear ethical guidelines, robust copyright protections, and fostering a collaborative human-AI workflow are crucial. The future isn’t about humans versus machines; it’s about humans *with* machines, crafting compelling stories that resonate with audiences for years to come. The challenge lies in ensuring that the human element – the heart and soul of storytelling – remains at the center of the creative process.
