Google io just added generative ai to search – Google I/O just added generative AI to search, and the internet just got a whole lot smarter (or maybe weirder? We’ll see!). This isn’t just a minor tweak; we’re talking a fundamental shift in how we find information online. Imagine search results that don’t just list links, but actually *understand* your query and synthesize answers from multiple sources. That’s the promise, at least. But will it deliver? We delve into the immediate impact, the tech behind it, and the potential for both awesome advancements and epic fails.
From the revamped search results page layout to the underlying AI models and algorithms, we’ll dissect Google’s ambitious leap into generative AI. We’ll explore the potential for bias, the user experience (both the good and the bad), and how this changes the competitive landscape. Get ready for a deep dive into the future of search – it’s going to be a wild ride.
Google I/O’s Generative AI Integration in Search
Google I/O 2023 brought a seismic shift to the search landscape with the integration of generative AI. No longer just a list of links, search is evolving into a conversational, more insightful experience. This integration represents a fundamental change in how we interact with information online, promising both exciting possibilities and some growing pains.
Immediate Effects on User Search Experience
The most immediate effect is a shift from a purely link-based search to a more comprehensive, context-aware one. Users now receive a concise, AI-generated summary at the top of the search results, providing a quick overview of the topic before diving into individual links. This summary acts as a filter, helping users quickly grasp the essence of their query and navigate relevant information more efficiently. Imagine searching for “best hiking trails near Yosemite.” Instead of a wall of links, you get a curated summary highlighting top trails, difficulty levels, and key features, followed by a list of more detailed resources. This significantly improves the speed and ease of finding information.
Changes to the Search Results Page Layout
The integration of generative AI has visibly altered the search results page. The traditional blue links still exist, but now they’re often preceded by a prominent, AI-generated snippet. This snippet typically includes a brief summary, key facts, and sometimes even visual elements like images or maps, directly related to the query. The layout prioritizes synthesized information, placing the AI’s response front and center, making it the primary point of interaction for many users. The overall look feels less like a list and more like an interactive conversation with the search engine.
Examples of Search Queries Handled with and without Generative AI
Let’s compare a simple search for “what is photosynthesis?” Without generative AI, the results would be a list of websites explaining the process. With generative AI, the user gets a concise, easy-to-understand explanation at the top, potentially with a diagram, followed by links to more in-depth resources. A more complex query like “compare the economic policies of FDR and Reagan” would benefit even more. Traditional search would yield a multitude of links, requiring the user to synthesize information. Generative AI, however, could present a comparative summary highlighting key differences and similarities, simplifying the research process significantly.
Comparison of Traditional Search vs. AI-Powered Search
| Feature | Traditional Search | AI-Powered Search |
|---|---|---|
| Speed | Fast for simple queries, slower for complex ones requiring synthesis. | Fast for both simple and complex queries, thanks to AI summarization. |
| Accuracy | Highly dependent on the quality and relevance of individual websites. | Accuracy depends on the AI model’s training data and ability to synthesize information; potential for biases and inaccuracies. |
| User Experience | Can feel overwhelming with many links; requires active filtering and synthesis. | More streamlined and intuitive; provides a quick overview and simplifies information gathering. |
| Information Presentation | List of links | Summary, key facts, links to detailed resources |
Technical Aspects of the Integration: Google Io Just Added Generative Ai To Search
Google’s integration of generative AI into its search functionality represents a significant leap forward, demanding a deep dive into the complex technical infrastructure supporting this innovative feature. This enhanced search experience relies on a sophisticated interplay of cutting-edge AI models, vast datasets, and rigorous bias mitigation strategies.
The underlying architecture is far from simple, involving multiple interconnected components working in harmony. Understanding these components is crucial to appreciating the power and potential limitations of this new search paradigm.
AI Models and Algorithms
The core of Google’s generative AI search lies in large language models (LLMs), likely variations of Transformer-based architectures like those powering LaMDA or PaLM 2. These models excel at processing and generating human-like text. The specific model used is likely a proprietary adaptation optimized for search queries, prioritizing accuracy, conciseness, and relevance above all else. The algorithms employed include techniques like attention mechanisms, allowing the model to focus on the most pertinent parts of the input query and associated knowledge base, and reinforcement learning from human feedback (RLHF), fine-tuning the model to align its responses with human expectations and preferences. This refinement process is iterative, constantly improving the quality and relevance of the search results.
Data Sources for Training and Refinement
Training such a sophisticated AI requires an enormous dataset. Google leverages its vast corpus of indexed web pages, books, articles, code, and other digital content. This massive dataset provides the model with the raw material needed to learn patterns, relationships, and contextual information. The training process involves pre-training on this general knowledge base, followed by fine-tuning on specific datasets relevant to search queries, such as those focused on factual accuracy and user intent. Regular updates and refinements are crucial to ensure the model stays current with evolving information and user needs. Think of it as constantly feeding the AI a never-ending stream of updated knowledge to keep it sharp and relevant.
Bias Mitigation Strategies
Generative AI models are susceptible to biases present in their training data. This means the AI might inadvertently reflect societal biases in its responses. Google employs several strategies to mitigate this risk. These include careful data curation to remove or reduce biased content, algorithmic adjustments to detect and counter biases in the model’s output, and rigorous testing and evaluation to identify and address biases in real-world scenarios. Furthermore, human oversight plays a critical role, with human reviewers evaluating the AI’s responses and providing feedback to refine the model and its bias mitigation strategies. The goal is to create a search experience that is fair, equitable, and unbiased.
Data Flow from Search Query to AI-Generated Response
The following flowchart illustrates the data flow:
[Imagine a flowchart here. It would start with a “User Search Query” box, leading to a “Query Processing & Understanding” box, then to a “Knowledge Base Retrieval” box (accessing Google’s indexed data). From there, a line would lead to the “Generative AI Model” box, which would then connect to a “Response Generation” box. Finally, a line would lead to a “Response Filtering & Bias Mitigation” box, culminating in an “AI-Generated Response” box presented to the user.] The flowchart visually represents the journey of a user’s search query through various stages of processing, leveraging the power of Google’s massive knowledge base and sophisticated AI model, all while implementing rigorous bias mitigation techniques. Each stage is essential to delivering a relevant, accurate, and unbiased response.
User Adoption and Feedback
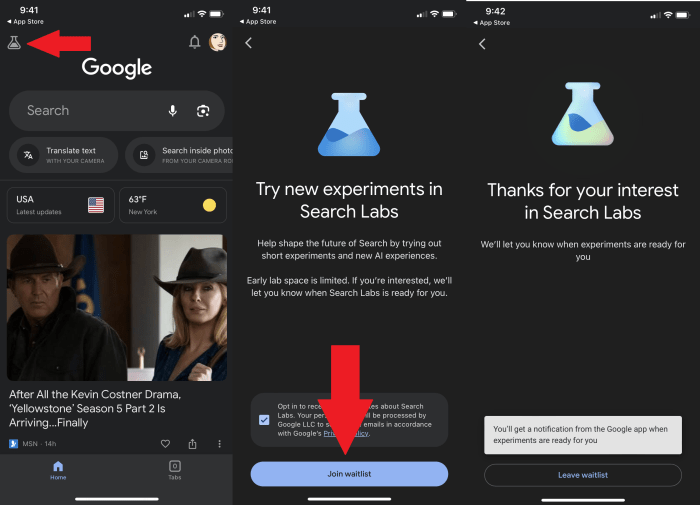
Source: pcmag.com
Google I/O’s generative AI integration into search is a game-changer, promising more intuitive results. But even with AI’s power, security remains paramount; consider the complexities highlighted in this insightful pinduoduo malware security roundup , a reminder that robust security measures are crucial alongside innovative tech like Google’s new AI. Ultimately, the future of search hinges on both innovation and unwavering security protocols.
Google’s integration of generative AI into its search engine has been met with a mixed bag of reactions, ranging from enthusiastic praise to cautious skepticism. Early adoption rates suggest a significant portion of users are intrigued by the new capabilities, but challenges remain in ensuring a smooth and intuitive user experience. Understanding user feedback is crucial for Google to refine the AI search feature and maximize its potential.
The initial rollout has provided valuable insights into user behavior and preferences, allowing Google to identify areas for improvement and address potential points of friction. Analyzing user engagement metrics alongside qualitative feedback offers a comprehensive view of the success of this significant update.
Positive User Feedback
Early user testimonials reveal a strong positive response to the enhanced search experience. Many users appreciate the AI’s ability to synthesize information from multiple sources, providing concise and comprehensive answers to complex queries. For example, users researching historical events have praised the AI’s capacity to present a nuanced overview, incorporating diverse perspectives and avoiding overly simplistic narratives. Others have found the AI particularly helpful in summarizing lengthy articles or comparing different products, saving them considerable time and effort. The ability to ask follow-up questions and refine search results iteratively has also been highlighted as a significant advantage, transforming the search process from a simple -based retrieval into a more interactive and conversational experience.
Areas of User Frustration and Confusion
Despite the positive feedback, several areas of user frustration have emerged. Some users report difficulty understanding the AI’s reasoning process, particularly when presented with nuanced or ambiguous queries. The AI’s responses, while often accurate, can sometimes lack the detailed citations and source information preferred by academic researchers or those requiring high levels of verification. Another common complaint revolves around the potential for inaccuracies or biases in the AI’s responses, highlighting the ongoing need for careful monitoring and refinement of the underlying algorithms. Furthermore, the visual presentation of the AI’s responses can occasionally be overwhelming, particularly for users accustomed to the more traditional search results pages.
User Engagement Metrics Comparison
While precise figures are not publicly available, anecdotal evidence and early reports suggest a noticeable increase in time spent on search engine results pages (SERPs) since the AI integration. This increase is likely attributable to the interactive nature of the new search experience, which encourages users to engage with the AI through follow-up questions and iterative refinement of their queries. Click-through rates (CTRs) on individual results, however, might have shown a slight decrease, as users find the AI’s synthesized answers sufficient to satisfy their information needs without needing to click through to individual websites. Further data analysis is required to confirm these trends and fully understand the impact of the AI integration on user engagement.
Suggested Improvements Based on Early User Feedback
Based on early user feedback, several improvements could enhance the user experience.
- Improved transparency regarding the AI’s sources and reasoning process.
- Enhanced mechanisms for fact-checking and verification of AI-generated responses.
- More intuitive visual presentation of AI-generated content, including better integration with traditional search results.
- Options for users to customize the level of detail and complexity in AI responses.
- Implementation of robust feedback mechanisms to allow users to easily report inaccuracies or biases.
Competitive Landscape and Future Implications

Source: googleapis.com
Google’s integration of generative AI into its search engine marks a pivotal moment in the ongoing battle for online information dominance. This isn’t just a feature update; it’s a strategic shift that could redefine how we interact with the internet, prompting a ripple effect across the entire search landscape and beyond. The implications are far-reaching, impacting not only search engine giants but also the way we access, process, and understand information.
The integration of generative AI into search is a game-changer, pushing the boundaries of what’s possible in information retrieval and significantly altering the competitive dynamics. Google’s approach, focusing on providing concise, informative answers directly within search results, contrasts with other players in the field. Microsoft’s Bing, for instance, has heavily leveraged OpenAI’s technology, offering a more conversational and expansive AI-powered search experience. DuckDuckGo, meanwhile, maintains its privacy-focused stance, albeit without the same level of generative AI integration. These differing approaches reflect varying strategic priorities and technological capabilities.
Comparison of Generative AI Approaches in Search Engines
Google’s approach prioritizes accuracy and conciseness, integrating generative AI to enhance existing search functionality. It aims to provide direct answers to complex queries, summarizing information from multiple sources. Bing, in contrast, utilizes a more conversational AI, enabling users to engage in extended dialogue with the search engine. This approach prioritizes a more interactive and exploratory search experience. DuckDuckGo, prioritizing user privacy, currently offers a more limited integration of AI-powered features, focusing on its core value proposition of enhanced user privacy. This diverse landscape demonstrates a variety of approaches to integrating generative AI into search, each with its own strengths and weaknesses.
Long-Term Effects on the Search Engine Market
The integration of generative AI is likely to intensify competition within the search engine market. Companies that effectively leverage this technology will be better positioned to attract and retain users. We might see a shift towards more conversational and interactive search experiences, with a greater emphasis on personalized results. Furthermore, the market may consolidate, with larger players acquiring smaller companies with specialized AI capabilities. The long-term impact will depend on factors such as user adoption, technological advancements, and regulatory developments. For example, Google’s significant market share might allow them to solidify their dominance, while competitors will need to innovate aggressively to maintain competitiveness.
Reshaping Online Information Access and Discovery
Generative AI in search has the potential to fundamentally reshape how we access and discover information online. Instead of sifting through numerous web pages, users may receive concise, synthesized answers directly within search results. This could lead to increased efficiency and improved information comprehension. However, challenges remain, including the need to address potential biases in AI models and ensure the accuracy and reliability of the information provided. The potential for misinformation and the ethical implications of AI-generated content are also critical considerations. For instance, imagine a scenario where a user researching a complex medical condition receives an inaccurate or misleading AI-generated response. This highlights the need for rigorous quality control and transparency in the development and deployment of these systems.
Timeline of Potential Future Developments
Within the next year, we can expect to see refinements in the accuracy and reliability of generative AI search results, along with improved personalization features. Within the next five years, expect widespread adoption of multimodal search, incorporating images, videos, and audio into the search process. Over the next decade, we may see the emergence of truly intelligent search assistants, capable of understanding complex queries and providing highly personalized and contextualized information. This timeline is, of course, speculative, and the actual pace of development will depend on technological advancements and market forces. For example, the development of more sophisticated natural language processing (NLP) models could accelerate the adoption of conversational AI in search. Conversely, regulatory hurdles or unexpected technological limitations could slow down progress.
Ethical Considerations and Societal Impact
Integrating generative AI into search engines presents a Pandora’s Box of ethical dilemmas, impacting everything from the spread of misinformation to the very fabric of the job market. The potential benefits are undeniable, but navigating the ethical minefield is crucial for responsible innovation. This section explores some key concerns and their potential consequences.
Misinformation and Disinformation
Generative AI’s ability to create realistic-sounding yet entirely fabricated content poses a significant threat to the spread of misinformation and disinformation. The ease with which AI can generate convincing fake news articles, reviews, or even scientific papers raises serious concerns about the trustworthiness of online information. This could lead to a further erosion of public trust in institutions and experts, potentially fueling social unrest and polarization. Imagine a scenario where a sophisticated AI generates a series of seemingly credible articles claiming a particular vaccine is dangerous, leading to widespread vaccine hesitancy and a public health crisis. The speed and scale at which such disinformation can spread through search results is alarming. Combating this requires robust fact-checking mechanisms and transparent labeling of AI-generated content, a challenge that requires both technological and societal solutions.
Impact on Search Engine Optimization () Industry, Google io just added generative ai to search
The integration of generative AI into search significantly alters the landscape. Traditional strategies, heavily reliant on optimization and link building, may become less effective as search results are increasingly shaped by AI’s understanding of user intent and context. This shift could lead to job displacement for specialists who lack the skills to adapt to AI-driven search optimization. Companies may need to invest heavily in retraining their teams, focusing on skills related to prompt engineering, AI content analysis, and understanding AI-driven search algorithms. A hypothetical example: a small agency specializing in optimization might struggle to stay competitive, losing clients to larger agencies that have successfully integrated AI-powered tools into their workflows. This transition could lead to a restructuring of the industry, favoring those who can harness the power of AI effectively.
Hypothetical Scenario: A Double-Edged Sword
Consider a future where generative AI powers search completely. On one hand, users benefit from highly personalized and efficient information retrieval. Imagine a doctor instantly accessing the latest research on a rare disease through a concise, AI-generated summary, leading to faster diagnosis and treatment. This represents a positive societal impact, enhancing efficiency and access to information. However, this same technology could also be used to create highly targeted disinformation campaigns, manipulating public opinion on sensitive topics like elections or public health crises. For example, an AI could generate tailored misinformation campaigns targeting specific demographics based on their search history and online behavior. This illustrates the dual nature of generative AI in search: a powerful tool for progress, but also a potential weapon for manipulation if not carefully managed.
Last Word
Source: contentatscale.ai
Google’s integration of generative AI into search is a game-changer, a bold move that could redefine how we interact with information. While the early days are filled with both excitement and uncertainty, the potential benefits – more intuitive search, faster access to synthesized information – are undeniable. However, navigating the ethical implications and potential pitfalls will be crucial. The coming months will be a fascinating test of Google’s ambition, and the impact on the search engine landscape will be felt for years to come. Buckle up, internet; it’s going to be a bumpy ride.



