Twitter encrypted dm signal whatsapp – Twitter encrypted DMs, Signal, and WhatsApp: the holy trinity of private messaging, right? Wrong. While all three offer some level of security, the reality is far more nuanced. This deep dive explores the cryptographic algorithms, security features, vulnerabilities, metadata collection practices, and user experiences of each platform, revealing surprising differences and highlighting the crucial trade-offs between convenience and true privacy. We’ll unpack the technical details, dissect potential attack vectors, and ultimately help you make informed choices about where your private conversations truly belong.
From end-to-end encryption comparisons and a detailed analysis of metadata handling to a discussion of open-source versus proprietary implementations, we’ll leave no stone unturned in our quest to understand the security landscape of these popular messaging apps. We’ll even look ahead to future trends in encrypted messaging and the potential impact of emerging technologies like post-quantum cryptography. Get ready to have your perceptions challenged – and maybe even change the way you think about digital security.
End-to-End Encryption Comparison
Securing private conversations in the digital age is paramount, and end-to-end encryption (E2EE) plays a crucial role. This comparison delves into the E2EE implementations of three popular messaging platforms: Twitter Direct Messages, Signal, and WhatsApp, highlighting their similarities and differences. Understanding these nuances is key to making informed choices about which platform best suits your privacy needs.
Encryption Protocols and Algorithms
Each platform employs distinct cryptographic algorithms to achieve E2EE. Signal, known for its robust security focus, utilizes the Signal Protocol, a sophisticated system built upon the Double Ratchet Algorithm. This algorithm combines forward secrecy (past messages remain confidential even if a key is compromised) with perfect forward secrecy (future messages remain confidential even if a key is compromised). WhatsApp, owned by Meta, also uses the Signal Protocol, benefiting from its security strengths. Twitter Direct Messages, on the other hand, uses AES-256 encryption, a widely adopted symmetric encryption algorithm. However, details about Twitter’s key exchange and other aspects of their implementation remain less transparent compared to Signal and WhatsApp.
Key Management and Exchange Mechanisms
The way keys are managed and exchanged is critical to E2EE’s effectiveness. Signal’s Signal Protocol uses a complex key exchange process involving Diffie-Hellman key exchange and other cryptographic techniques to establish secure communication channels. WhatsApp, leveraging the same protocol, shares this robust key management system. While Twitter uses AES-256, specifics regarding their key exchange mechanisms are not publicly available, leaving room for speculation regarding their security robustness. The lack of transparency surrounding Twitter’s key management is a notable weakness compared to the open and well-documented approaches of Signal and WhatsApp.
Metadata Handling and Privacy Implications
Beyond the encryption itself, metadata—data about the communication, not the content—plays a significant role in user privacy. While Signal and WhatsApp strive to minimize metadata collection, focusing on message delivery timestamps and recipient information, Twitter’s metadata collection practices are less transparent. The amount of metadata collected by Twitter for Direct Messages, including IP addresses and connection times, could potentially be used to infer information about users and their communications, raising privacy concerns.
Comparative Table of Encryption Implementations
| Platform Name | Encryption Type | Key Management | Metadata Collected |
|---|---|---|---|
| Signal | Signal Protocol (Double Ratchet Algorithm, Curve25519, AES-256, SHA-256) | Diffie-Hellman key exchange, pre-keys | Minimal (timestamps, recipient information) |
| Signal Protocol (Double Ratchet Algorithm, Curve25519, AES-256, SHA-256) | Diffie-Hellman key exchange, pre-keys | Minimal (timestamps, recipient information) | |
| Twitter Direct Messages | AES-256 | Details not publicly disclosed | Potentially more extensive than Signal and WhatsApp (IP addresses, connection times, etc.) |
Strengths and Weaknesses of Each Platform’s Encryption
Signal’s and WhatsApp’s use of the Signal Protocol represents a significant strength, offering a high level of security with well-vetted cryptographic algorithms and transparent key management. The open-source nature of the Signal Protocol allows for independent audits and scrutiny, further bolstering its trustworthiness. However, even with strong encryption, metadata collection can still pose privacy risks. Twitter’s use of AES-256 is a standard and secure algorithm, but the lack of transparency regarding its key management and metadata collection practices represents a significant weakness. This lack of transparency makes it difficult to assess the true level of security provided by Twitter Direct Messages.
Security Features and Vulnerabilities: Twitter Encrypted Dm Signal Whatsapp
The seemingly simple act of sending a message carries a surprising amount of security baggage. While platforms like Twitter, Signal, and WhatsApp offer varying levels of encryption, they’re not invulnerable. Understanding their strengths and weaknesses is crucial for navigating the digital landscape safely. This section dives into the security features of each platform, highlighting potential vulnerabilities and outlining strategies for safer messaging.
Each platform boasts unique security features, but none are impenetrable. Factors like user behavior and platform-specific weaknesses contribute significantly to the overall security posture. The following analysis explores these aspects for Twitter, Signal, and WhatsApp, emphasizing the importance of proactive security measures.
So, you’re worried about privacy? We get it. Twitter’s encrypted DMs, Signal, and WhatsApp all offer varying levels of security, but even the strongest encryption can’t always guarantee safety. Consider the recent toyota leak vehicle data security roundup ; it highlights how even massive corporations can struggle with data protection. Ultimately, understanding the limitations of each platform and practicing good digital hygiene remains key to protecting your info, whether it’s on Twitter or anywhere else.
Twitter Security Features and Vulnerabilities
Twitter’s security primarily relies on HTTPS for data transmission between the user and the server. However, the platform’s reliance on third-party apps and its open nature introduces significant vulnerabilities. Direct messages (DMs) are end-to-end encrypted, but this protection is easily bypassed if a user falls prey to phishing scams or malware. A sophisticated attacker could potentially exploit vulnerabilities in third-party apps integrated with Twitter to gain unauthorized access to user data, including DMs. A hypothetical attack scenario could involve a malicious actor creating a seemingly legitimate app that requests extensive permissions, then using those permissions to steal user data or compromise accounts. The consequences could include account takeover, identity theft, and the exposure of private communications. Best practices for secure messaging on Twitter include using strong, unique passwords, enabling two-factor authentication, being wary of suspicious links and apps, and regularly reviewing connected accounts and app permissions.
Signal Security Features and Vulnerabilities
Signal, designed with privacy as a core principle, utilizes end-to-end encryption for all messages and calls. This means only the sender and receiver can access the content. However, vulnerabilities still exist. A successful attack could involve compromising a user’s device through malware or exploiting a software flaw in the Signal app itself. A hypothetical attack could involve a sophisticated piece of malware that captures screenshots or keystrokes, thereby exposing the content of Signal messages even with end-to-end encryption. This type of attack, while challenging, highlights the importance of device security. Best practices for Signal include regularly updating the app, using a strong passcode on your device, and avoiding jailbreaking or rooting your phone, as these actions compromise the device’s security.
WhatsApp Security Features and Vulnerabilities
WhatsApp, like Signal, employs end-to-end encryption for most communications. However, the platform’s metadata, such as timestamps and contact information, is not encrypted. This metadata can reveal valuable information about communication patterns. Moreover, WhatsApp’s integration with Facebook raises privacy concerns, as user data may be shared with Facebook’s broader ecosystem. A hypothetical attack could involve a man-in-the-middle attack targeting unencrypted metadata, allowing an attacker to track communication patterns and potentially infer sensitive information. The consequences could include surveillance and targeted attacks. Best practices for WhatsApp include regularly updating the app, enabling two-factor authentication, reviewing privacy settings, and limiting the sharing of personal information.
Metadata Analysis

Source: behance.net
So, you’ve cracked the encryption, right? Wrong. Even with end-to-end encryption, messaging apps still collect metadata – information *about* your messages, not the content itself. This seemingly minor detail can reveal a surprising amount about your communication habits and relationships. Let’s dive into the shadowy world of metadata and see how Twitter, Signal, and WhatsApp stack up.
The level of metadata collected significantly impacts user privacy. While end-to-end encryption protects the content of your messages, the metadata trail can still expose sensitive information about your connections and activities. Think of it like this: the encryption protects the letter’s contents, but the postmark, sender’s address, and recipient’s address are still visible. This metadata, while seemingly innocuous, can be pieced together to create a comprehensive profile of your digital life.
Metadata Collected by Each Platform
The three platforms – Twitter, Signal, and WhatsApp – each handle metadata differently. Understanding these differences is crucial to making informed choices about which platform best protects your privacy. A crucial distinction lies in the design philosophy of each platform: Twitter is a public social network, while Signal and WhatsApp prioritize privacy. This core difference is reflected in their metadata collection practices. We’ll examine the types of metadata gathered during transmission and storage of encrypted direct messages.
- Twitter: Twitter collects a substantial amount of metadata, including timestamps of messages, IP addresses of both sender and recipient, device information, and potentially even the length of messages (even if encrypted). Because Twitter is built around public interaction, this higher level of metadata collection is inherent to its functionality.
- Signal: Signal prioritizes privacy. Its metadata collection is significantly less extensive. While timestamps might be logged (though often with less precision), the focus is on minimizing the collection of identifying information. IP addresses are likely less persistently logged, and device information is minimized.
- WhatsApp: WhatsApp, owned by Meta, falls somewhere in between. While it offers end-to-end encryption for messages, it still collects metadata such as timestamps, phone numbers of participants, and potentially connection information. The extent of this collection is less transparent than Signal’s, but likely more than Twitter’s due to its focus on personal connections and group communication.
Implications for User Privacy
The differences in metadata collection have significant implications for user privacy. The more metadata collected, the greater the potential for inferring sensitive information about users and their communications. For example, the frequency and timing of messages between two users could reveal the nature of their relationship, even without access to the message content itself. Similarly, IP address data, even if not directly linked to a user’s identity, could be used to approximate their location. These seemingly small pieces of information, when aggregated, can paint a disturbingly detailed picture of an individual’s life.
Comparison of Metadata Collection
To further clarify the differences, let’s lay it out in a simple table:
| Feature | Signal | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Timestamps | High Precision | Lower Precision | Moderate Precision |
| IP Addresses | Collected | Minimized | Collected |
| Device Information | Collected | Minimized | Collected |
| Message Length | Potentially Collected | Not Collected | Not Collected |
| Contact Information | Potentially Collected (if public) | Not Collected | Collected (Phone Numbers) |
User Experience and Privacy Trade-offs
Source: fossbytes.com
Balancing user-friendliness with robust privacy features is a constant challenge for messaging platforms. While end-to-end encryption is crucial for security, overly complex interfaces can deter users from adopting and utilizing these essential privacy protections. This section explores how Twitter, Signal, and WhatsApp navigate this delicate balance, highlighting the trade-offs users face.
The user experience surrounding privacy settings and encryption varies significantly across these platforms. WhatsApp, for instance, offers a relatively straightforward interface for enabling end-to-end encryption, which is enabled by default for all chats. However, granular control over privacy settings, such as controlling who can add you to groups or see your last seen status, requires navigating several menus. Signal, known for its privacy-centric design, prioritizes simplicity in its encryption implementation; the encryption is always on, and there’s little user interaction needed. Twitter, on the other hand, presents a more fragmented experience. Direct messages (DMs) are encrypted, but the platform’s broader design prioritizes public engagement, leaving users to navigate a more complex landscape to understand and manage their privacy in different contexts.
Ease of Use and Accessibility of Privacy Features
The accessibility and ease of use of privacy features directly impact user adoption. Signal’s straightforward approach makes it easy for even technically unsophisticated users to understand and benefit from its strong encryption. WhatsApp, while generally user-friendly, presents a somewhat less intuitive path to advanced privacy settings, potentially leaving users unaware of or unable to fully leverage the available privacy controls. Twitter’s approach is the most complex; understanding the implications of its DM encryption within the context of its broader, publicly oriented design requires a more significant level of digital literacy. For example, a user might easily enable end-to-end encryption on WhatsApp, but might miss the option to control who can see their profile picture. Similarly, a user might easily send a direct message on Twitter, but might not fully grasp the implications of the encryption in relation to the public nature of the platform.
Trade-offs Between User Experience and Privacy
Each platform presents unique trade-offs between user experience and privacy. WhatsApp’s balance leans toward user-friendliness, sacrificing some granular control over privacy settings for a simpler overall experience. This might mean a user is unaware of all the privacy features available, resulting in potential vulnerabilities. Signal prioritizes privacy, leading to a streamlined but potentially less feature-rich experience compared to WhatsApp. The simplicity, however, reduces the likelihood of users making unintentional privacy compromises. Twitter’s approach demonstrates a different trade-off; the platform prioritizes public engagement and ease of use for its broader functionality, which means that managing privacy in the context of DMs requires a more conscious effort from the user. This means users may be less likely to fully utilize the encryption features, or even understand their implications fully. A user might choose WhatsApp for its familiar interface and numerous features, even if Signal offers stronger privacy controls in a less user-friendly package. This highlights the inherent tension between ease of use and the effective utilization of privacy features.
Open Source vs. Proprietary Implementations
The transparency of a messaging app’s encryption implementation significantly impacts user trust and overall security. Open-source projects allow for independent verification and community scrutiny, while proprietary systems rely on the vendor’s claims. This comparison explores the contrasting approaches of Twitter, Signal, and WhatsApp, highlighting the strengths and weaknesses of each.
The level of transparency varies drastically across these platforms. Signal, being entirely open-source, boasts the highest level of community scrutiny. Its codebase is publicly available, enabling independent security researchers to audit the implementation, identify vulnerabilities, and contribute improvements. This open nature fosters a collaborative security model, leading to quicker identification and patching of potential weaknesses. In contrast, WhatsApp, while employing end-to-end encryption, keeps its core encryption implementation proprietary. While WhatsApp publishes security white papers, the lack of access to the source code limits the extent of independent verification. Twitter’s approach is even more opaque; while they use encryption for DMs, the specifics of their implementation are largely undisclosed, leaving users to rely solely on their assurances.
Transparency and Community Scrutiny
Signal’s open-source nature allows for extensive community scrutiny. Independent researchers regularly audit the code, contributing to a robust and well-vetted security posture. This contrasts sharply with WhatsApp’s proprietary approach, where verification relies primarily on the company’s published security white papers and internal testing. Twitter’s lack of transparency in this area represents the lowest level of scrutiny, leaving users with limited independent verification of their encryption claims. The community’s ability to identify and report vulnerabilities is directly tied to the level of code accessibility.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Open-Source vs. Proprietary Implementations
Open-source implementations, like Signal’s, benefit from a multitude of independent reviews and contributions, improving security and fostering trust. However, this transparency can also expose the system to potential attacks if vulnerabilities are discovered before being patched. Proprietary implementations, such as WhatsApp’s, offer better protection against malicious actors exploiting vulnerabilities before they are fixed, but the lack of independent verification can lead to a decreased level of user trust. The trade-off lies between the benefits of community oversight and the potential risks of immediate vulnerability exposure.
Public Access to Source Code and Security Audits
Signal provides complete and readily accessible source code, facilitating independent security audits by experts and the broader community. This proactive approach strengthens user confidence and allows for rapid identification and remediation of security flaws. WhatsApp, while regularly publishing security white papers, maintains a proprietary implementation, limiting the scope of independent audits. Twitter offers the least transparency, with minimal publicly available information regarding their DM encryption implementation and no known independent security audits. The differences in accessibility directly influence the level of trust users can place in each platform’s security claims.
Future Trends in Encrypted Messaging
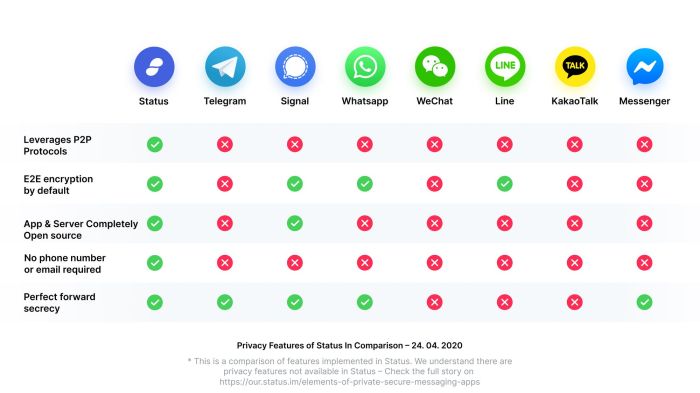
Source: status.im
The landscape of secure communication is constantly evolving, driven by advancements in cryptography and a growing awareness of privacy concerns. The future of encrypted messaging hinges on addressing emerging threats and leveraging new technologies to enhance security and user experience. This evolution necessitates a proactive approach, anticipating challenges and capitalizing on opportunities presented by the technological landscape.
The next generation of encrypted messaging will be defined by its ability to withstand increasingly sophisticated attacks and seamlessly integrate with other privacy-enhancing technologies. We can expect a convergence of various approaches, leading to more robust and user-friendly solutions that go beyond simple end-to-end encryption.
Post-Quantum Cryptography’s Impact, Twitter encrypted dm signal whatsapp
The advent of quantum computing poses a significant threat to current encryption standards. Quantum computers, with their immense processing power, could potentially break widely used encryption algorithms like RSA and ECC, rendering current encrypted messaging vulnerable. Post-quantum cryptography (PQC) aims to develop algorithms resistant to attacks from both classical and quantum computers. The transition to PQC in encrypted messaging platforms will be a gradual but crucial process. For instance, the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) is currently evaluating and standardizing several PQC algorithms, and their adoption by major messaging platforms will be a pivotal step in ensuring long-term security. This transition will require careful planning and significant investment to ensure compatibility and maintain seamless user experience. Successful implementation will depend on the efficient integration of new algorithms into existing infrastructure, balancing security improvements with performance considerations.
Future Developments in Encrypted Messaging
The following potential advancements are expected to shape the future of secure messaging:
Several key areas will drive innovation in encrypted messaging. These improvements will not only bolster security but also enhance the overall user experience and expand the capabilities of secure communication platforms.
- Enhanced Metadata Protection: Current end-to-end encryption primarily focuses on protecting message content. Future developments will likely concentrate on minimizing metadata exposure, such as timestamps and recipient lists, which can still reveal sensitive information about communication patterns. Techniques like differential privacy and federated learning could play a significant role in achieving this.
- Improved Key Management: Secure key management is paramount. Future systems might incorporate more robust key exchange protocols and decentralized key management systems to mitigate risks associated with single points of failure or compromised servers.
- Integration with Decentralized Technologies: Blockchain technology and decentralized identity systems offer the potential for enhanced privacy and security. Integrating these technologies could enable secure messaging without reliance on centralized servers, reducing the risk of data breaches and censorship.
- AI-Powered Security Enhancements: Artificial intelligence can play a crucial role in detecting and mitigating emerging threats. AI algorithms could be used to identify and block malicious actors, detect sophisticated phishing attempts, and enhance the overall security posture of messaging platforms.
- Improved Interoperability: Lack of interoperability between different encrypted messaging platforms is a significant limitation. Future developments could focus on creating standardized protocols and frameworks to allow seamless communication between users on various platforms, enhancing overall security and user convenience.
Final Wrap-Up
Choosing the “best” encrypted messaging app isn’t a simple matter of picking the one with the fanciest features. It’s about understanding the subtle differences in how each platform handles your data, its inherent vulnerabilities, and the trade-offs you’re willing to make between convenience and privacy. By weighing the strengths and weaknesses of Twitter DMs, Signal, and WhatsApp, you can make an informed decision about which platform best protects your sensitive conversations. Remember, your privacy is your responsibility, so choose wisely.



