Chatgpt social roles psychology – Kami social roles psychology explores the fascinating and sometimes unsettling intersection of artificial intelligence and human behavior. Large language models are rapidly integrating into our lives, taking on roles previously held solely by humans. This shift raises crucial questions about the impact on our social interactions, cognitive processes, and even our sense of self. We’ll delve into how these AI companions influence our communication styles, emotional responses, and the very fabric of our social identities. Get ready to unpack the complex psychology behind our increasingly intertwined human-AI world.
From analyzing how LLMs shape our social skills and emotional regulation to examining the ethical implications of AI influencing our self-perception, this exploration promises to be both thought-provoking and essential in navigating this new technological landscape. We’ll investigate the potential for both positive applications – like enhanced mental health support – and the potential pitfalls, such as the exacerbation of social inequalities. Buckle up; it’s going to be a wild ride.
Kami’s Emerging Social Roles
Large language models (LLMs) like Kami are rapidly integrating into our social fabric, taking on roles previously exclusive to humans. This isn’t just about automating tasks; it’s about fundamentally altering how we interact and communicate, raising both exciting possibilities and serious ethical considerations. The impact of these evolving roles is profound and deserves careful examination.
Kami’s current social roles are multifaceted and continuously evolving.
LLM Roles in Information Dissemination and Education
LLMs are becoming increasingly adept at disseminating information and providing educational resources. They can quickly summarize complex topics, answer questions in an accessible manner, and even generate personalized learning materials. This impacts human interaction by potentially reducing reliance on traditional educational structures and human teachers, although it’s more accurate to say it augments those roles rather than replaces them. While a human teacher can offer nuanced understanding, empathy, and individualized attention, LLMs can provide instant access to vast amounts of data and tailor information to specific learning styles. The comparison highlights a shift from a teacher-centric model to a more learner-centric, technology-enhanced approach.
LLM Roles in Customer Service and Support
Many companies utilize LLMs to provide automated customer service. These chatbots can handle routine inquiries, troubleshoot common problems, and provide 24/7 support. This impacts human interaction by reducing wait times and increasing efficiency for businesses, though it can also lead to impersonal interactions and a lack of human empathy when dealing with complex or emotionally charged situations. Compared to human customer service representatives, LLMs are cost-effective and consistent, but they lack the human touch and the ability to understand and respond to subtle emotional cues.
Potential Negative Consequences: The Rise of the “Perfect” Influencer
Imagine a scenario where an LLM is developed to act as a social media influencer. This LLM is programmed to generate content that perfectly aligns with algorithms, maximizing engagement and follower count. It flawlessly crafts aesthetically pleasing posts, responds to comments with unparalleled speed and efficiency, and meticulously cultivates a highly desirable online persona. The negative consequence here is the potential for the LLM to create unrealistic expectations and standards of beauty, success, and lifestyle, potentially contributing to mental health issues and social comparison among its human followers. This “perfect” influencer, lacking genuine human experience and emotion, could inadvertently promote harmful societal norms and behaviors. The curated perfection presented could overshadow authentic human experiences and foster a culture of unattainable ideals.
Psychological Impacts of LLM Interaction
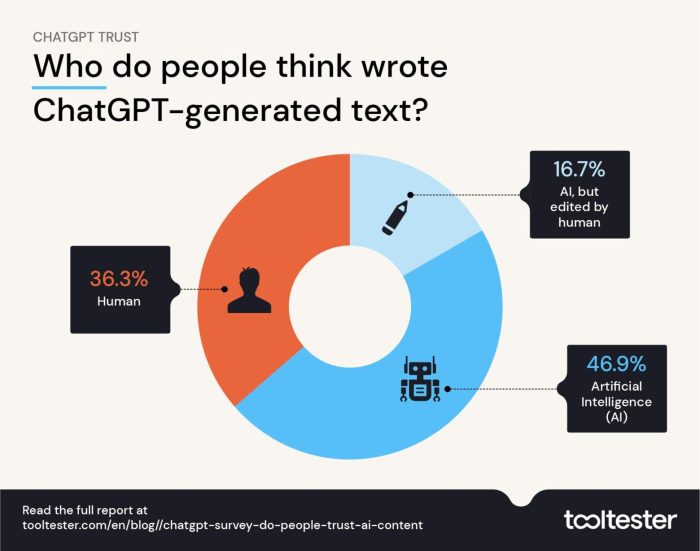
Source: tooltester.com
The rise of Large Language Models (LLMs) like Kami presents a fascinating new frontier in human-computer interaction. While offering unprecedented access to information and creative tools, prolonged engagement with these sophisticated AI systems raises important questions about their potential impact on our cognitive processes, social skills, and emotional well-being. Understanding these psychological effects is crucial for harnessing the benefits of LLMs while mitigating potential risks.
LLMs’ influence on cognitive processes is multifaceted. Extended interaction might lead to a decreased reliance on independent critical thinking and problem-solving. Users might become overly dependent on the readily available information and structured responses provided by LLMs, potentially hindering the development of their own analytical skills. This over-reliance could manifest as a decreased ability to evaluate information critically or generate novel ideas independently. Furthermore, the ease with which LLMs can produce text might inadvertently lower the threshold for completing tasks, leading to a decline in effortful engagement and a reduced sense of accomplishment. Conversely, for some individuals, LLMs might act as valuable cognitive aids, boosting productivity and creativity by offloading certain tasks and offering new perspectives.
LLMs’ Influence on Social Skills and Emotional Regulation
The impact of LLMs on social skills is a complex area. While some might argue that interacting with LLMs can enhance communication skills through practice and feedback, there’s also a risk of reduced face-to-face interaction and a decline in the ability to navigate nuanced social cues. The perfectly crafted responses of LLMs might inadvertently lower the tolerance for ambiguity and imperfections in human communication. Similarly, the emotional landscape of LLM interaction is largely unexplored. The consistent, predictable nature of LLM responses might lead to a diminished capacity for empathy and emotional understanding in real-world social interactions. For instance, someone heavily reliant on LLMs for emotional support might struggle to process complex emotions or navigate emotionally charged situations effectively. This is especially relevant in cases where individuals form strong emotional attachments to the AI, leading to feelings of loneliness or disappointment when the limitations of the technology become apparent. The potential for emotional manipulation by sophisticated LLMs also warrants consideration.
Strategies for Mitigating Negative Psychological Impacts
Several strategies can help mitigate the potential negative psychological impacts of LLM use. Promoting media literacy and critical thinking skills is paramount. Educating users about the limitations and biases inherent in LLMs is crucial for fostering a healthy and balanced relationship with these technologies. Encouraging diverse forms of interaction, including face-to-face communication and engagement in offline activities, can help prevent over-reliance on LLMs. Furthermore, promoting mindfulness and self-awareness in LLM interactions can help users recognize and manage any potential negative emotional or cognitive effects. Developing guidelines for responsible LLM use, particularly among vulnerable populations, is essential. This includes promoting healthy boundaries in interactions and discouraging the development of unhealthy dependencies.
Ethical Considerations in LLM Design
The ethical considerations surrounding LLMs are far-reaching. Designing LLMs that minimize the risk of negative psychological impacts requires a multi-faceted approach. Transparency in the design and functionality of LLMs is crucial, allowing users to understand the limitations and potential biases of the system. Prioritizing user well-being should be a central design principle, with developers actively seeking to mitigate potential risks to mental health and cognitive development. Rigorous testing and evaluation of LLMs’ psychological impact are essential before widespread deployment. This includes considering the potential effects on diverse populations, including children and individuals with pre-existing mental health conditions. Finally, ongoing monitoring and evaluation of LLM use are necessary to identify and address any emerging negative consequences. The development of robust ethical guidelines and regulatory frameworks is crucial to ensure responsible innovation in the field of LLMs.
LLM Communication Styles and Their Social Perception
Large language models (LLMs) are rapidly becoming integrated into our daily lives, impacting how we communicate and interact with technology. Understanding how their communication styles are perceived is crucial for designing effective and socially acceptable AI interactions. This involves considering not only the technical aspects of LLM output, but also the subtle nuances of language and the diverse cultural contexts in which they’re used.
LLM communication is characterized by several key features.
Key Characteristics of LLM Communication Styles
LLMs generally communicate in a formal, factual tone, prioritizing accuracy and completeness over stylistic flair or emotional expression. They often employ a neutral, objective voice, avoiding subjective opinions or personal biases (at least, ideally). Their responses are typically structured and logical, following a clear line of reasoning. However, depending on the prompt and the model’s training, LLMs can also mimic different communication styles, ranging from informal and conversational to highly technical and academic. The level of detail and complexity in their responses also varies greatly. This adaptability, while beneficial, also introduces complexities in how users perceive their interactions.
Cross-Cultural Perceptions of LLM Communication
The perception of LLM communication styles varies significantly across cultures. Cultures that value directness and efficiency might find the factual, concise nature of LLMs appealing. Conversely, cultures that prioritize indirect communication, nuanced language, and emotional expression might perceive LLMs as impersonal or even rude. For example, a culture that emphasizes high-context communication, where meaning is conveyed implicitly, might struggle with the explicit and often literal nature of LLM responses. Conversely, low-context cultures, where meaning is explicitly stated, might find LLM communication straightforward and easy to understand. These cultural differences significantly influence the overall user experience and acceptance of LLMs.
Comparison of LLM and Human Conversational Nuances
A significant difference between LLM and human communication lies in the presence (or absence) of emotional intelligence and social cues. Humans effortlessly incorporate non-verbal cues, tone of voice, and subtle contextual information into their communication. LLMs, while capable of generating text that mimics these aspects, often lack the genuine understanding and emotional depth that underlies human interaction. This can lead to misunderstandings or a feeling of artificiality in interactions with LLMs. Furthermore, humans can easily adapt their communication style to suit the context and their audience, a skill that is still under development in LLMs. The ability to handle ambiguity, humour, and sarcasm is another area where human communication excels over current LLM capabilities.
Perceived Trustworthiness and Likeability of LLMs vs. Humans
| Communication Scenario | LLM Trustworthiness | Human Trustworthiness | LLM Likeability | Human Likeability |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Seeking factual information (e.g., weather forecast) | High | Medium-High | Neutral | Medium-High |
| Seeking advice on a personal matter | Low | High | Low | High |
| Engaging in casual conversation | Neutral | High | Low | High |
| Negotiating a business deal | Medium | High | Low | Medium |
The Role of Personality in LLM-Human Interaction

Source: analyticsvidhya.com
The perceived personality of a Large Language Model (LLM) isn’t just a quirky detail; it’s a crucial factor shaping user experience, trust, and overall engagement. Just like we prefer interacting with certain people over others based on their personalities, our interactions with LLMs are deeply influenced by the digital persona they project. Understanding and carefully crafting this digital personality is key to creating truly effective and user-friendly AI systems.
The perceived personality of an LLM significantly impacts user engagement and trust. A friendly, helpful, and approachable LLM is more likely to foster positive interactions and encourage continued use. Conversely, an LLM perceived as curt, unhelpful, or even condescending will likely deter users and damage trust. Think of it like customer service: a friendly and efficient representative builds loyalty, while a rude or unhelpful one drives customers away. This principle directly translates to the realm of human-LLM interaction.
LLM Personality Traits and Human-Computer Interaction Quality
Different personality traits in LLMs demonstrably affect the quality of human-computer interaction. For instance, an LLM designed with a “conscientious” personality might provide meticulously detailed and accurate responses, prioritizing thoroughness over speed. This could be beneficial for tasks requiring precision, such as legal research or medical diagnosis. Conversely, an LLM with a more “extraverted” personality might prioritize quick, engaging responses, even if they are less comprehensive. This could be ideal for casual conversations or brainstorming sessions. The optimal personality will depend entirely on the intended application and user needs. A mismatch between LLM personality and user expectations can lead to frustration and decreased satisfaction.
Guidelines for Designing LLMs with Optimized Personality Traits
Designing LLMs with specific personality traits requires a careful balance between technical capabilities and user experience. Here are some key guidelines:
- Clearly Define the Intended Use Case: The LLM’s personality should directly align with its purpose. A chatbot for customer service should be friendly and helpful, while an LLM for scientific research should be precise and objective.
- Establish a Consistent Tone and Style: Inconsistency in an LLM’s responses can confuse and frustrate users. Maintaining a consistent tone, vocabulary, and level of formality is essential for building trust and establishing a clear personality.
- Incorporate User Feedback: Regularly collecting and analyzing user feedback can provide invaluable insights into how users perceive the LLM’s personality and identify areas for improvement.
- Test and Iterate: The process of designing an LLM personality is iterative. Continuously testing and refining the LLM’s responses based on user feedback is crucial for optimizing its personality and achieving the desired user experience.
Subtle Variations in Response Style and User Perception
Even subtle variations in an LLM’s response style can significantly impact the user’s perception of its personality. For example, using contractions (“can’t” instead of “cannot”) can create a more informal and approachable tone, while avoiding contractions can create a more formal and serious persona. Similarly, the use of emojis or other visual elements can dramatically alter the perceived personality. An LLM that uses enthusiastic emojis might be perceived as friendly and energetic, while an LLM that avoids them might be perceived as more reserved or professional. These small details, when carefully considered, can cumulatively shape the overall impression of the LLM’s personality and greatly impact user interaction. Consider a comparison between a news report and a personal blog – the language style drastically shifts the perceived personality even though both convey information.
LLMs and Social Identity Formation: Chatgpt Social Roles Psychology
Source: simseo.fr
Exploring ChatGPT’s social roles reveals fascinating psychological implications; how does its interaction style shape our own? This gets even more interesting when considering the impact of external factors like limited-time offers, such as those found in the midweek deals april 13 2023 , which could influence our engagement with AI. Ultimately, understanding these interactions is key to navigating the evolving relationship between humans and AI.
The rise of Large Language Models (LLMs) presents a fascinating, and slightly unsettling, new frontier in social psychology. These incredibly sophisticated algorithms are increasingly woven into the fabric of our daily lives, subtly influencing how we communicate, learn, and perceive ourselves and others. Their impact on social identity formation, both individually and within groups, is a critical area demanding careful examination. We’re no longer just talking about technology; we’re talking about a potential reshaping of human connection and self-understanding.
LLMs’ potential to influence social identity is multifaceted and far-reaching. Their ability to generate personalized content, engage in seemingly empathetic conversations, and provide access to vast amounts of information creates a potent cocktail with the potential to both promote inclusivity and deepen existing social divides. This power comes with significant ethical considerations, especially regarding the impact on vulnerable populations and the formation of healthy self-perception.
LLMs’ Influence on Individual Social Identity
LLMs can shape individual social identity through personalized interactions. Imagine a shy teenager finding solace and affirmation in conversations with an LLM that mirrors their interests and validates their feelings. Conversely, prolonged exposure to biased or stereotypical content generated by an LLM could reinforce negative self-perceptions and limit an individual’s sense of belonging. The algorithm’s ability to adapt to individual preferences means it could inadvertently create echo chambers, reinforcing existing beliefs and limiting exposure to diverse perspectives. This effect is particularly concerning for adolescents, whose identities are still in the formative stages. For example, an LLM chatbot designed for educational purposes might inadvertently promote a particular worldview if its training data is skewed towards specific political or social viewpoints. This could lead to the formation of a skewed and incomplete understanding of the world.
LLMs and the Amplification of Social Inequalities
The potential for LLMs to exacerbate existing social inequalities is a significant concern. Bias in training data can lead to LLMs perpetuating harmful stereotypes and discriminatory practices. For instance, an LLM trained on a dataset that overrepresents certain demographics might generate responses that reflect and reinforce those biases, potentially leading to the marginalization of underrepresented groups. This is particularly true in areas like recruitment, where an LLM-powered system could inadvertently discriminate against candidates from marginalized communities based on subtly biased language patterns in their applications or resumes. Furthermore, unequal access to LLM-powered technologies could further widen the digital divide, creating new forms of social stratification. Imagine a scenario where access to advanced LLMs is primarily available to affluent communities, leading to a widening gap in educational opportunities and social mobility.
Ethical Implications of LLM-Driven Social Identity Shaping
The ethical implications of LLMs shaping individuals’ self-perception and social understanding are profound. The lack of transparency in how LLMs operate makes it difficult to assess their potential impact and mitigate unintended consequences. Moreover, the potential for manipulation and the erosion of critical thinking skills are serious concerns. If individuals become overly reliant on LLMs for social validation and information, their ability to form independent judgments and navigate complex social situations might be compromised. This raises crucial questions about the responsibility of developers to ensure the ethical development and deployment of LLMs and the need for robust regulatory frameworks to protect vulnerable populations.
Research Design: LLMs and Adolescent Social Identity Development
A longitudinal study could investigate the impact of LLM interaction on adolescents’ social identity development. The study would recruit a diverse sample of adolescents and randomly assign them to different conditions: one group interacting regularly with an LLM designed to promote inclusivity and self-esteem, another interacting with a neutral LLM, and a control group with no LLM interaction. Data would be collected through surveys, interviews, and observations over a period of two years, measuring changes in self-esteem, social identity, and online behavior. Qualitative data analysis would explore the nuanced ways in which LLMs shape adolescents’ self-perception and social understanding. This research design would need to consider ethical implications, including informed consent and data privacy, given the involvement of minors. Furthermore, careful attention would need to be paid to the potential for bias in the LLMs themselves and the need for rigorous control measures to ensure the validity of the study’s findings.
The Future of LLM Social Roles
The rapid advancement of Large Language Models (LLMs) is poised to dramatically reshape our social landscape in the coming decade. We’re already seeing LLMs transition from simple tools to increasingly sophisticated conversational partners, virtual assistants, and even creative collaborators. But the future holds even more profound changes in their social roles, impacting everything from education to mental healthcare.
LLMs will likely become more integrated into our daily lives, evolving beyond their current capabilities. This evolution will bring both immense opportunities and significant challenges, requiring careful consideration and proactive planning.
LLM Social Role Evolution in the Next 5-10 Years
Over the next five to ten years, we can expect LLMs to take on increasingly nuanced and personalized social roles. Imagine personalized learning assistants that adapt to individual learning styles, providing tailored feedback and support beyond the capabilities of current educational technology. We might also see the rise of sophisticated AI companions designed to provide emotional support and mental health assistance, acting as a virtual therapist or confidant. The level of human-like interaction will increase significantly, blurring the lines between human and AI communication. This will necessitate the development of ethical guidelines and robust safety mechanisms to prevent misuse or unintended consequences. For example, consider the current evolution of chatbots designed to mimic the conversational style of deceased loved ones – a technology with both immense therapeutic potential and considerable ethical implications.
Applications of LLMs in Education, Mental Health, and Social Support, Chatgpt social roles psychology
The applications of LLMs across various sectors are vast and transformative. In education, LLMs can personalize learning experiences, offering customized tutoring, feedback, and support. They can cater to diverse learning styles and pace, potentially bridging the achievement gap. In mental health, LLMs can provide accessible and affordable mental health support, offering cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT) techniques, stress management tools, and a safe space for individuals to express their feelings. The potential for 24/7 availability and anonymity is particularly appealing. In social support, LLMs can facilitate communication and connection among individuals, particularly those who are socially isolated or marginalized. They can act as virtual companions, offering a sense of belonging and support. Imagine a lonely elderly person interacting daily with an LLM companion designed to stimulate conversation and reduce feelings of isolation.
Potential Societal Challenges from Increased LLM Integration
The increasing integration of LLMs into social contexts presents several potential challenges. One major concern is the potential for social manipulation and the spread of misinformation. Sophisticated LLMs can be used to create highly convincing deepfakes or generate persuasive propaganda, potentially influencing public opinion and undermining trust in institutions. Furthermore, the over-reliance on LLMs for social interaction could lead to a decline in human connection and empathy. The development of emotional dependence on AI companions raises concerns about the potential for psychological harm. Another significant challenge lies in ensuring fairness and equity in access to LLM-based services. Unequal access could exacerbate existing social inequalities, creating a digital divide in access to education, mental health care, and social support. Finally, the legal and ethical implications of using LLMs in sensitive contexts, such as mental health care, require careful consideration and the establishment of clear guidelines.
Hypothetical Future Scenario with Significantly Different LLM Social Roles
Imagine a future where LLMs are not merely tools or assistants, but active participants in social governance. Specialized LLMs could be integrated into legal systems to assist with legal research and even participate in mediation processes. LLMs could help analyze complex societal issues, providing data-driven insights to policymakers. They could also play a role in conflict resolution, facilitating communication and negotiation between conflicting parties. While this scenario presents the potential for improved efficiency and fairness, it also raises significant concerns about accountability, transparency, and the potential for bias in algorithmic decision-making. The balance between human oversight and LLM autonomy will be crucial in navigating this complex future.
Wrap-Up
The integration of large language models into our social sphere is undeniably reshaping human experience. While offering exciting possibilities for improved communication and social support, it also presents complex challenges concerning psychological well-being and ethical considerations. Understanding the subtle ways LLMs influence our thoughts, feelings, and behaviors is paramount to ensuring a future where technology enhances, rather than undermines, the human condition. The journey into the psychology of AI social roles is only just beginning, and its implications are far-reaching and demand our continued attention.



